PCMCIAWho are PCMCIA?
PCMCIA (Personal Computer Memory Card International Association) is an
association of nearly 500 companies sharing a computer industry background. Their aim is
to set standards for non-proprietary PC Card™ technology providing expansion options
for, primarily, notebook and portable computers. The very nature of portable computer
systems dictates the requirement for ever smaller and lighter expansion options including
memory, storage and I/O cards.
What are PCMCIA Cards™?
PCMCIA cards measure 54.0mm wide and 85.6mm deep (the approximate size
of a credit card) and fall into three categories: Type I, Type II and Type III. The three
categories denote the thickness of the card, and as this places a restriction on the
available space for electrical / mechanical components, it also governs the ultimate
application range. For example, considering the mechanical components required for a hard
disk drive, this application would require a Type III card. In all other respects Type I,
II and III cards are identical which means that thin cards may be used in thicker slots
but thick cards may not be used in thinner slots. Cards are designed to be user-plugable
devices and can be exchanged without the need to remove the system case.
Type I Card (3.3mm thick)
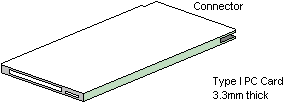 |
Common usage: |
RAM Memory
Flash Memory
One-Time Programmable Memory
EEPROM |
Type II Card (5.0mm thick)
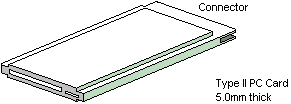 |
Common usage: |
Memory Enhancement
Data / Fax Modem
LAN & Host Communications |
Type III Card (10.5mm thick)
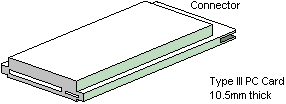 |
Common usage: |
Memory Enhancement
Data / Fax Modem
LAN & Host Communications
Removable Hard Disk Drives
Radio Communications |
PCMCIA Card Features
Socket Service software at the system BIOS level acts as an interface
between other software and the underlying hardware. It identifies the number of physical
card sockets provided in the system and reports the insertion and removal of cards while
the machine is running. Power and ground contacts on the card are the longest connectors
on the physical interface to ensure data integrity when devices are hot plugged. For
example, it is possible to down load a file into system memory via a modem, exchange the
communications card for a hard disk card and save the data without powering the system
down. Each PC Card™ contains information describing its characteristics and
capabilities. This is used by the system software to correctly configure the card for the
host system.
PCMCIA Standards
PCMCIA provides a definition of the interface between the card and
socket fitted to the host system.
| Release 1.0 |
September 1990 saw the first version of the PCMCIA standard. It defined
a memory card interface and supported such memory as DRAM and Flash RAM. |
| Release 2.0 |
In September 1991 support was added for I/O capabilities allowing for
LAN adapters, data / fax modems and disks. |
| Release 2.1 |
Release 2.1 added software support (Card Services & Socket
Services) to allow cards to be configured automatically. |
 
|

