Electricity At Work Regulations 1989 (S.I. 635)
See Also IPB 4115
The above regulations require that all electrical systems be constructed
and maintained so as to prevent danger at all times.
As part of Apricot's manufacturing process, all units are subjected to
strict electrical safety testing before they are allowed to leave the factory.
For the benefit of employers who may wish to re-verify their equipment
to ensure continued compliance with the above regulations, we have listed below details of
the tests that are carried out on all of our production units.
All of the tests listed are carried out as part of our overall product
approval process and are monitored, controlled, and defined by various International
Regulatory Bodies. Under normal circumstances no damage will occur to the systems when
these tests are carried out, but it should be borne in mind that these tests require
specialist equipment and test procedures.
Some of the tests listed employ dangerous voltages and currents, hence
tests should only be carried out by experienced personnel in controlled environments.
This test is used to verify that all accessible metalwork is securely
connected to the main earth terminal of the unit under test.
A 6 volt DC supply providing a current flow of 27 Amperes is applied to
the main Earth terminal and each of the accessible metal parts of the unit. The system
must not have any resistive path of greater than 0.1 ohms between the main earth terminal
and the point under test.
(During this test the resistance of the mains lead is ignored.)
| 2: |
Insulation Resistance Test. |
This test is used to verify that the resistance between the mains supply
terminals and any metal part is sufficiently high enough to prevent electric shock.
A voltage of 500V DC is applied to the p roduct between the primary
earth terminal and the Live and Neutral terminals which have been connected together. The
resistance measured must be more than 4 Megohms.
| 3: |
Insulation Strength (Dielectric Strength) Test. |
This test is used to verify the integrity of the insulation used within
the isolating parts of the equipment.
A voltage of 2.2KV DC is applied between the primary earth terminal and
the Live and Neutral terminals, which have been connected together. In the case of
double-insulated products, the test is carried out between the supply terminals and the
equipment housing or secondary circuit. In this latter test the voltage is increased to
5KV. The voltage is applied for 3 seconds minimum and no breakdown or "flash
over" must occur. This test may be carried out using AC voltages, but Filter
Capacitors within the PSU may give false or misleading readings.
This test is used to measure the current which passes down the earth
wire under normal use. Such currents are usually dependant on the type of filtering
components used within the product.
The current between Live and Neutral terminals with respect to earthed
metal is measured. The combined total of Live to Earth and Neutral to Earth must be less
than 3.5mA.
Detailed below are the Earth Bond Test Points that should be referred to
during test number 2. For system units fitted with a thin wire Ethernet connector it
should be noted that, as part of the IEEE 802.3 Ethernet specification, a building network
should only be earthed at one point. The thin wire Ethernet connector is therefore
isolated from earth and will fail the earth bond test (this is correct).
LANstation (Test Points)
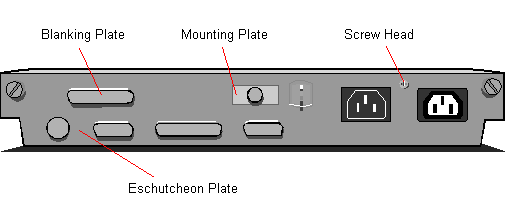
XEN-LS (Test Points)

Qi (Test Points)
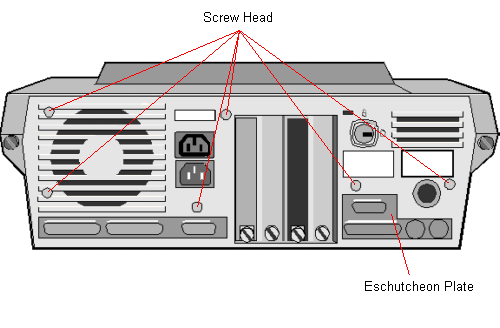
FTe (Test Points)
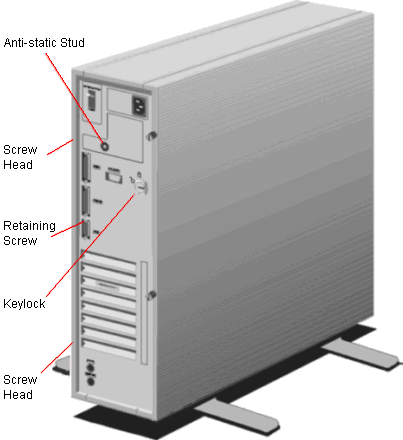
FTs (Test Points)

|


