 |













|
|
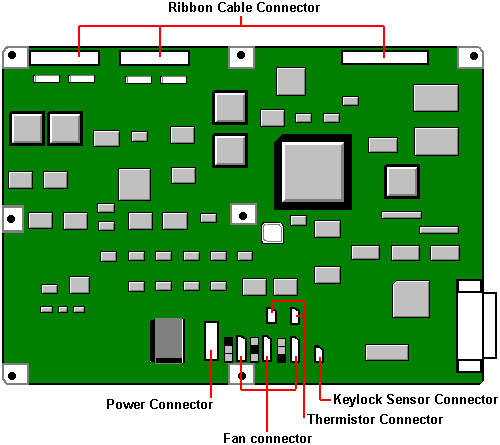
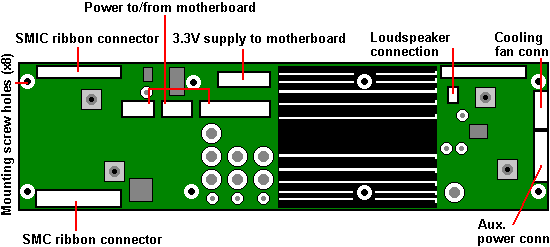
FT4200 'Discovery'
Motherboard Layout (Rev 1.13.1)
Memory
Server memory is located in two memory banks on the motherboard. Fully
loaded, these banks provide 2 Gbytes of common high-speed memory for the server. Each bank
can hold 1, 2, or 4 ECC Dual In-line Memory modules (DIMMs). All DIMMs in a bank must be
the same. There are advantages in fitting two or four DIMMs into a bank as two way and
four way interleave become available.
Read performance
No. of DIMMs |
Interleave |
Page miss + Precharge |
Page miss |
Page hit |
Page hit burst data rate |
four |
4 : 1 |
14:1:1:1 |
11:1:1:1 |
8:1:1:1 |
194 Mb/s |
two |
2 : 1 |
14:2:2:2 |
11:2:2:2 |
8:2:2:2 |
152 Mb/s |
one |
1 : 1 |
14:4:4:4 |
11:4:4:4 |
8:4:4:4 |
107 Mb/s |
The above is based upon 60ns DRAM and a
system clock of 66MHz
Write performance
No. of DIMMs |
Interleave |
Page miss + Precharge |
Page miss |
Page hit |
four |
4 : 1 |
10 |
7 |
7 |
two |
2 : 1 |
11 |
8 |
8 |
one |
1 : 1 |
16 |
13 |
13 |
 
System Management Interface Card

 
System Management Controller
 
Motherboard Power
Distribution Board
 
Add-Ins
| Processor expansion |
|
| Pentium Pro at 200MHz, 256KByte cache |
XB58374 |
| Dual Pentium Pro at 200MHz, 512KByte cache per CPU |
HB57837 |
| Redundant Power Supply |
|
| N+1 Redundant power supply upgrade (includes
one power module) ** |
XB012 |
| Additional power modules for the above |
SU58493 |
| Battery backup unit to go with the above ** |
SU57750 |
| ** Must be fitted by an Apricot Hardware Certified Engineer |
|
| Memory (Multiples of) |
|
| 32MB upgrade |
HA57829 |
| 64MB upgrade |
HA57830 |
| Network options |
|
| 3Com 10/100 PCI Ethernet card (3C905TX) |
XB59527 |
| 3Com AUI to UTP Transceiver (3C583) |
XB50900 |
| 3Com PCI Ethernet Combo card (3C900) |
XB59526 |
| Specialix serial cards |
|
| 4 port terminal adaptor |
XB43319 |
| 8 port terminal adaptor |
XB43320 |
| 32-port EISA SI/XIO serial card |
XB54610 |
| 8 port modular terminal adaptor |
XB54611 |
| 8 port modular terminal adaptor (7 RS232, 1 parallel) |
XB54612 |
| 128-port EISA RIO serial card |
XB54613 |
| 8 port remote terminal adaptor |
XB54614 |
| 8 port remote terminal adaptor (7 RS232, 1 parallel) |
XB54615 |
| SCSI controllers |
|
| Adaptec AHA2940uw
Single Channel Ultra Wide SCSI Disk Controller |
XB58023 |
| SCSI cable set |
HB57831 |
| DPT PM 3334uw SmartRaid
Ultra Wide SCSI Controller (3 channel) |
HB58024 |
| RAID cable set |
HB57832 |
| 4MB Raid Cache Upgrade |
HA55494 |
Disk Drives
| MB |
Make |
Model |
Type |
Part Number |
| 4,550 |
Quantum |
HN4550J |
FAST/WIDE SCSI (See Note below) |
HB58476 |
| 9,100 |
Quantum |
HN91J |
FAST/WIDE SCSI (See Note below) |
HB58477 |
| TAPE DRIVES |
|
|
|
| 12-24GB |
HP |
HP
C1537A |
DDS III |
SU61220 |
| 72-144GB |
HP |
HP
C1557A Autoloader |
DDS III |
SU61226 |
| 20-40GB |
Quantum |
DLT4000 |
SCSI |
HA55474 |
| CD ROM |
|
|
|
|
|
Panasonic |
CR-506-B |
SCSI |
15830931 |
| Note |
FAST & WIDE SCSI |
|
SCSI was originally developed as a bus that transferred up to 5 Mbytes
per second: this bus was 8 bits wide. The transfer rate was doubled to 10 Mbytes per
second and the term FAST was introduced. The 8 bit bus was then developed into a 16 bit
bus which doubled the transfer rate to 20 Mbytes per second and this development was
called WIDE. Hence the term FAST & WIDE SCSI on Shogun. |
|
80 Pin SCSI Drive Technology |
|
The Shogun uses an SCA connector ( Single Connector Attachment ) on the
SCSI disk drive interface. This 80 pin SCA connector includes the 16 bit wide SCSI bus
plus the DC power and ID addressing, allowing optimum engineering access for the Shogun
HOT PLUG technology. |
 
Jumper Settings
BIOS Recovery
1 - 2 |
Recover |
2 - 3 |
Normal |
Clear BIOS settings
1 - 2 |
Normal |
3 - 4 |
> 1 sec. discharge |
Floppy drive mode
1 - 3 |
2 - 4 |
3-mode operation (Japan only) |
| |
3 - 4 |
Normal 2-mode operation |
SW1 - Bus clock multiplier settings
External bus clock
Frequency |
SW1-5 |
SW1-6 |
66MHz |
off |
on |
60MHz |
on |
off |
50MHz |
on |
on |
Processor bus multiplier
SW1-1 |
SW1-2 |
SW1-3 |
SW1-4 |
Factor |
on |
on |
off |
on |
x2 |
on |
off |
off |
on |
x2.5 |
on |
on |
on |
off |
x3 |
on |
off |
on |
off |
x3.5 |
on |
on |
off |
off |
x4 |
on |
off |
off |
off |
x4.5 |
 
Rear Panel
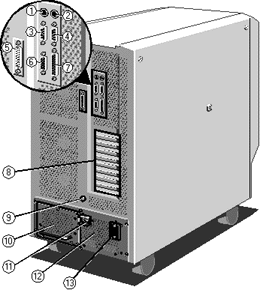 |
| 1 |
Keyboard connector |
| 2 |
Mouse connector |
| 3 |
Serial port - COM 1 |
| 4 |
Serial port - COM 2 |
| 5 |
SMC serial port |
| 6 |
Video connector |
| 7 |
Parallel port |
| 8 |
Expansion Slot Openings |
| 9 |
Stud for Anti-Static Strap |
| 10 |
Removable UPS Battery Pack |
| 11 |
UPS External Isolator Switch |
| 12 |
Uninterruptible Power Supply |
| 13 |
Mains Power Socket |
|
 
CMOS Discharge
Clear BIOS settings
1 - 2 |
Normal |
3 - 4 |
> 1 sec. discharge |












 
Interrupts, DMA and Memory
Memory Map
| Address Range (hex) |
Amount |
Function |
| 0000,0000 - 0003,FFFF |
256 KB |
Base system memory (fixed) |
| 0004,0000 - 0007,FFFF |
256 KB |
Base system memory (fixed) |
| 0008,0000 - 0009,FFFF |
128 KB |
Base system memory or ISA memory enabled in
Setup |
| 000A,0000 - 000B,FFFF |
128 KB |
ISA video DRAM |
| 000C,0000 - 000E,FFFF |
192 KB |
Off board video BIOS (can be shadowed)
AIC-7870 SCSI BIOS (can be shadowed) |
| 000F,0000 - 000F,FFFF |
64 KB |
ISA memory, system BIOS (fixed) |
| 0010,0000 - 00EF,FFFF |
14 MB |
System memory or unused |
| 00F0,0000 - 00FF,FFFF |
1 MB |
System memory or EISA/ISA memory |
| 0100,0000 - 3FFF,FFFF |
1008 MB |
System memory or unused |
| 4000,0000 - BFFF,FFFF |
1024 MB |
EISA memory or I/O slave memory |
| C000,0000 - C1FF,FFFF |
32 MB |
Memory mapped math coprocessor |
| C200,0000 - FEBF,FFFF |
944 MB |
EISA memory or I/O slave memory |
| FEC0,0000 - FEC0,0FFF |
4 KB |
I/O APIC #1 |
| FEC0,1000 - FEC0,1FFF |
4 KB |
I/O APIC #2 |
| FEC0,2000 - FEC0,2FFF |
4 KB |
I/O APIC #3 |
| FEC0,3000 - FEC0,3FFF |
4 KB |
I/O APIC #4 |
| FEC0,4000 - FFDF,4FFF |
32752 KB |
EISA memory or I/O slave memory |
| FFE0,0000 - FFFF,FFFF |
32 KB |
EISA (BIOS/ECU) |
I/O Map
| 0000 - 001F |
DMA Controller 1 |
| 0020 - 0021 |
Interrupt Controller 1 |
| 0022 - 0023 |
EISA bridge config. space access ports |
| 0024 - 0025 |
AIP configuration space access ports |
| 0026 - 0027 |
Configuration Space Access Ports |
| 0040 - 005F |
Programmable Timer |
| 0060, 0064 |
Keyboard Controller |
| 0061 |
NMI Status & Control Register |
| 0070 |
NMI Mask (bit 7) & RTC Address (bits 6:0) |
| 0071 |
Real Time Clock (RTC) |
| 0080 - 008F |
DMA Low Page Register |
| 0092 |
System Control Port A (PC-AT control Port) |
| 00A0 - 00BF |
Interrupt Controller 2 |
| 00C0 - 00DF |
DMA Controller 2 |
| 00F0 |
Clear NPX error |
| 00F8 - 00FF |
x87 Numeric Coprocessor |
| 0102 |
Video Display Controller |
| 0170 - 0177 |
Secondary Fixed Disk Controller (IDE) |
| 01F0 - 01F7 |
Primary Fixed Disk Controller (IDE) |
| 0220 - 022F |
Serial Port |
| 0238 - 023F |
Serial Port |
| 0278 - 027F |
Parallel Port 3 |
| 02E8 - 02EF |
Serial Port 2 |
| 02F8 - 02FF |
Serial Port 2 |
| 0338 - 033F |
Serial Port 2 |
| 0370 - 0375 |
Secondary Floppy |
| 0376 |
Secondary IDE |
| 0377 |
Secondary IDE / Floppy |
| 0378 - 037F |
Parallel Port 2 |
| 03B4 - 03BA |
Monochrome Display Port |
| 03BC - 03BF |
Parallel Port 1 (Primary) |
| 03C0 - 03CF |
Enhanced Graphics Adapter |
| 03D4 - 03DA |
Colour Graphics Controller |
| 03E8 - 03EF |
Serial Port |
| 03F0 - 03F5 |
Floppy Disk Controller |
| 03F6 - 03F7 |
Primary IDE - Sec. Floppy |
| 03F8 - 03FF |
Serial Port 1 (Primary) |
| 0400 - 043F |
DMA Controller 1, Extended Mode Registers |
| 0461 |
Extended NMI / Reset Control |
| 0462 |
Software NMI |
| 0464 |
Last EISA Bus master granted |
| 0480 - 048F |
DMA High Page Register |
| 04C0 - 04CF |
DMA Controller 2, High Base Register |
| 04D0 - 04D1 |
Interrupt Controllers 1 & 2 Control Register |
| 04D4 - 04D7 |
DMA Controller 2, Extended Mode Register |
| 04D8 - 04DF |
Reserved |
| 04E0 - 04FF |
DMA Channel Stop Registers |
| 0678 - 067A |
Parallel Port (ECP) |
| 0778 - 077A |
Parallel Port (ECP) |
| 07BC - 07BE |
Parallel Port (ECP) |
| 0800 - 08FF |
NVRAM |
| 0C80 - 0C83 |
EISA System Identifier Registers |
| 0C84 |
Board Revision Register |
| 0C85 - 0C86 |
BIOS Function Control |
| 0CF8 |
PCICONFIG_ADDRESS Register |
| 0CFC |
PCICONFIG_DATA Register |
| n000 - n0FF |
EISA Slot n I/O Space |
| x100 - x3FF |
ISA I/O slot alias address |
| n400 - n4FF |
EISA Slot n I/O Space (n = 1 to 15) |
| x500 - x7FF |
ISA I/O slot alias address |
| n800 - n8FF |
EISA Slot n I/O space (n = 1 to 15) |
| x900 - xBFF |
ISA I/O slot alias address |
| nC00 - nCFF |
EISA Slot n I/O Space (n = 1 to 15) |
| xD00 - xFFF |
ISA I/O slot alias address |
| 46E8 |
Video Display Controller |
EISA Slot Assignments
0 |
System Board |
1 - 8 |
EISA expansion boards |
9 - A |
Embedded SCSI |
B |
Memory module |
C |
Memory module (expansion module) |
D |
Primary PCI segment |
E |
CPU1 module |
F |
CPU2 module |
Direct Memory Access Channels
0 |
(add-in board) |
1 |
(add-in board) |
2 |
Diskette drive |
3 |
IDE hard disk drive |
4 |
Reserved |
5 |
(add-in board) |
6 |
(add-in board) |
7 |
(add-in board) |
ISA Interrupts
NMI |
Parity Error |
0 |
Interval timer |
1 |
Keyboard buffer full |
2 |
Reserved, cascade interrupt from slave PIC |
3 |
Onboard serial port B (COM2), if enabled |
4 |
Onboard serial port A (COM1), if enabled |
5 |
Parallel port LPT2, if enabled |
6 |
Onboard diskette (floppy) controller, if enabled |
7 |
Parallel port LPT1, if enabled |
8 |
Real-time clock (RTC) |
9 |
Video |
10 |
COM3; if enabled, it can be set for EISA add-in boards
using the SCU |
11 |
COM4; if enabled, it can be set for EISA add-in boards
using the SCU AIC-7870; if enabled, it can be set for EISA add-in boards using the SCU |
12 |
Onboard PS/2 mouse port, if enabled |
13 |
Math coprocessor error |
14 |
IDE hard drive controller, if enabled |
15 |
User definable; using the SCU, it can be set for the
following:  EISA add-in boards EISA add-in boards
 IDE hard drive
controller IDE hard drive
controller
 onboard video,
programmable to 9, 10, 11, or 15 onboard video,
programmable to 9, 10, 11, or 15
 onboard SCSI,
programmable to 9, 10, 11, or 15 (SCU limits SCSI to three choices) onboard SCSI,
programmable to 9, 10, 11, or 15 (SCU limits SCSI to three choices)
|
 
Uninterruptible Power Supply
The Uninterruptible Power Supply is a self-contained battery-backed unit
which supplies the system unit with all its power requirements. The following is a list of
its major features:
 1000W
maximum total DC output 1000W
maximum total DC output
 Auto-ranging AC input
voltage selection Auto-ranging AC input
voltage selection
 48V DC input from
backup batteries 48V DC input from
backup batteries
 Battery power circuit
breaker Battery power circuit
breaker
 Constant voltage
battery charging output Constant voltage
battery charging output
 Remote control /
monitoring facility Remote control /
monitoring facility
 Cooling fans mounted
on, and powered from, the power supply Cooling fans mounted
on, and powered from, the power supply
 Compliance with all
relevant safety standards Compliance with all
relevant safety standards
 
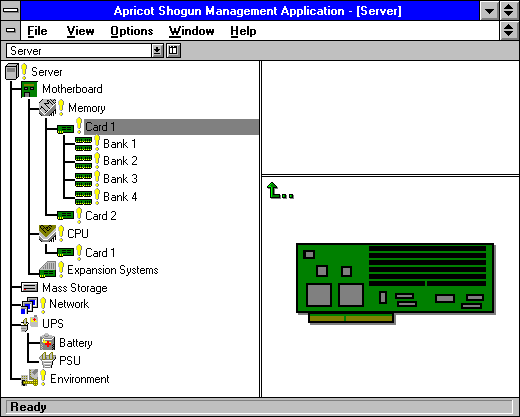
Apricot System Management Application
 
|


